Gone are the days when simple, manual systems generated a profit. 21st-century traders and brokers rely on complex digital tools and algorithms. They use these tools to implement and adjust automated trading strategies.
Algotrade gained recognition among both the US and European brokers.
Even more surprising, small businesses are more likely than large firms to adopt Algotrade toolkits.
Small companies need that competitive edge.
Finely tuned automation software is key to accurately executing trade orders under limited resources. Budget size becomes less significant.
Automated trading strategies help monetize internal expertise, test waters, or exploit market imperfections. Every strategy uses inside trade bots provided by trading platforms, specific off-the-shelf solutions, or tailor-made software.
In this post, we identify the most common trade automation algorithms that are used within a complex automated trading strategy.
Side note. A custom trading platform is possible within 1,880 – 3,467 working hours, starting at $50,000 – $100,000. Check out how to build a trading platform to learn what it takes to launch your own solution.
1
What is an Automated Trading System?
Automated trading means brokers shift all or certain order placement and execution processes to specialized software applications. These applications make trades based on pre-defined instructions.
When using an automated trading application, brokers set up rules regarding price, time, volume, etc. The application scans the market for suitable opportunities, checking multiple conditions simultaneously. When market parameters match the criteria traders have pre-set in automated trading strategies, it alerts the responsible person. Or it executes the order without human supervision and intervention.
The software reduces the large amount of manual work required to monitor the market. Plus, accuracy and speed of execution increase—both critical for certain operations.
Based on the number of criteria used for the execution rules, automated trading strategies vary from simple to very complex.
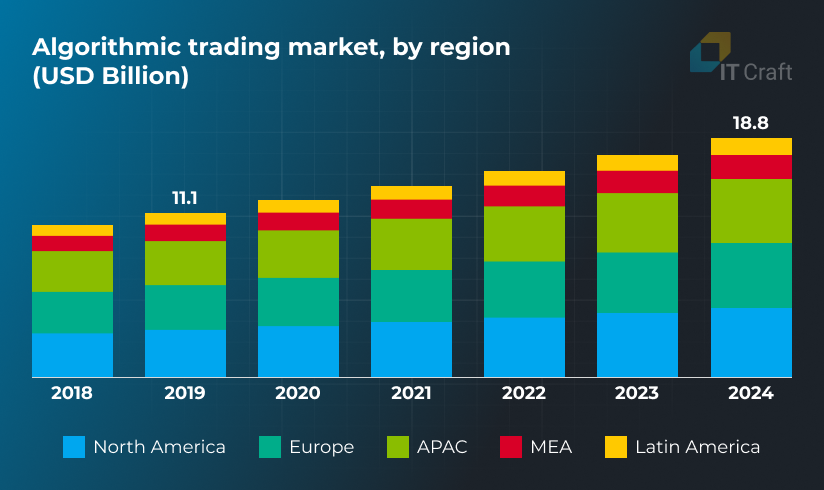 Source: https://www.marketsandmarkets.com/Market-Reports/algorithmic-trading-market-179361860.html
Source: https://www.marketsandmarkets.com/Market-Reports/algorithmic-trading-market-179361860.html
2
Automated Trading vs. Algorithmic Trading: What is the Difference?

Traders often use both terms to designate the same concept. However, they do not exactly match.
All automated trades are algorithmic, but not all algorithmic trades are automated.
An algorithmic trade means traders apply formulas and models to define trading rules and steps. They build a scenario, test it on historical data, and deploy it in real-life trade.
Automation degree—manual, semi-automated, fully automated—varies.
Traders determine how the app will behave based on conditions defined in the automated trading strategy. For instance, the software automatically places orders at the beginning of a month but never closes deals. It will autonomously close deals when fully automatic. Meanwhile, it will autonomously close deals upon reaching a specific price range—thus optimizing the timing of order execution.
Programming has more to offer traders when they look for answers to “how to automate my trading system in the best way?”
AI draws on vast data volumes the trade market generates every second. It helps identify complex patterns and significant variables. Software developers use ML algorithms to improve forecast accuracy.
This makes it possible to discern deviations in the price curve from pure randomness and react to developing market trends earlier.
Advanced automated trading strategies become available with the help of trading software development.
Do you want to increase profits by using an automated trading system?
We can help. Let’s discuss requirements.
Contact us
3
Most Common Automated Trading Strategies
Traders use automation strategies to buy/sell at a higher price, improve entry time, and/or hedge against losing positions.
The following strategies are highly automatable, thus widely implemented in automated trading systems:
Time-Series Momentum (Trend-Based)
Time-series momentum focuses on whether a specific market is moving up or down. This strategy prioritizes assets based on their past performance. Traders keep growing assets. They get rid of those showing negative momentum.
In short, “buy high, sell higher.” Traders buy and keep assets showing positive growth during a specific period. The key to success is identifying winning/losing assets early in the up/down cycle.
Timing makes the difference between profit and losses. It is essential to review if the trend continues. Traders must aggregate historical data and compare it to current parameters. Trade automation tools allow collecting then making sense of market data. They can also highlight signs of potential change in trend direction.
Time-series momentum strategy generates profits for most implementations. This makes it possible to achieve extreme profits. Still, it is market-dependent, requiring expertise and constant risk control. Diversification in portfolio construction and rebalancing are critical for hedging risks.
Cross-Sectional Momentum
This momentum strategy takes relative performance into account. It means concentrating on top-performing assets while shorting bottom market performers. Just like time-series momentum, cross-sectional momentum works for up markets.
“Buy best, sell worst.” Traders approach momentum from a slightly different angle. They list top X market performers and cut off Y laggards based on past performance. Timing is less critical: traders assign the same number of assets to each portfolio.
Neither momentum strategies perform well in down markets. Hence, it is critical to identify established, actual trends in both cases. Trading software helps automatically gather relevant market data and generate insights. Traders make sense of data reports then decide. Or they simply create automated sales/purchases upon reaching pre-determined values.
Cross-sectional momentum shows the best results in currency markets.
Combining cross-sectional and time-series momentum as part of a hedging strategy makes sense.
Dollar-Cost Averaging
Dollar-cost averaging is a practice of investing equal sums into the same asset regularly over a certain period. It aims at lowering long-term asset costs. Price at a certain point does not matter for this strategy. Consistency is crucial.
Traders spend a fixed amount of money every time instead of the entire sum within a single session. They buy a different number of assets each time, depending on their market price at the purchase time. Traders profit from market declines.
Dollar-cost averaging allows a decrease in median purchase costs per asset. It increases investing discipline and minimizes regrets by sticking to the initial plan. Hence, traders can set up an automated purchase of selected positions.
Yes, it is regarded as the best strategy for novices and those who are not interested in continually monitoring the market. It removes pitfalls of inopportune timing and counter-productive decisions backed by investors’ emotions.
Market Making Strategy
This is a short-term strategy. It focuses on making money on the spread—the difference between selling and purchase price. Market makers strive to make as many operations as possible and as fast as feasible.
Traders who stick to the market-making strategy buy and sell positions at the same time. They sell a position immediately once they receive an order from a buyer. This way, market makers ensure market liquidity and minimize risks of changed price direction.
Small lots nowadays are traded electronically. Traditionally, traders negotiate large lots on the phone. However, large traders also tend to opt for online solutions (e.g., using Limpid Markets for precious metal swap) due to decreased negotiation time and operation costs.
As mentioned above, market makers earn money on the spread. Hence, they are profitable when handling large volumes. They also hedge risks by setting spread. Large spreads are a distinct feature of a new market. Established, high-liquid markets have tight spreads.
Day Trading Automation
Day trading strategy targets short-term market volatility. Traders enter and exit positions within the same day. In extreme cases, they hold a position for only seconds.
Traders must determine profit and stop-loss levels. They might simply sell a position upon reaching a pre-determined level or decide on a more complex technique. A well-thought-out strategy and risk management, including a maximum loss limit, are critical when a trader does not want to go bankrupt after several unsuccessful bids.
Traders use various software to spot trends and potential entry points. They can set up automated sales/purchases as part of an automated trading strategy. Constant manual chart monitoring can be exhausting, especially when dealing with several positions simultaneously—but not for software.
This strategy does not suit everyone. It requires extensive market knowledge, dedication, and a cool head.
Also, traders must keep in mind that taxes and transactional costs also decrease profit margins. (For instance, IT Craft helps develop and maintain trading platform. It offers trade bots that always count commissions to eliminate end users’ losses.)
Arbitrage Strategy
The arbitrage strategy aims at capitalizing on a price imbalance that might emerge when several markets list the same asset. Traders buy an asset at a lower price in one market and sell it higher in another.
The fundamental assumption behind the arbitrage trading strategy: prices do not fluctuate from their fair value for long.
Complex mathematical models are used to encounter price deviations and buy assets immediately outpacing price amendment. Traders will sell them on another market/platform or later in the same market when the price returns to its average value.
Arbitrage strategy is mostly automated because price amendments happen fast. Human traders may not even detect slight deviations. Yet, computer algorithms spot discrepancies at a glance and exploit them until sellers run out of positions or correct them.
Traders consider arbitrage a low-risk strategy. Still, arbitrage cannot be the only strategy: it does not work for high-frequency trades. Also, traders must pay attention to transaction costs. Those might lead to insignificant profits.
4
The Most Profitable Strategy in Automated Trading
When building a winning automated trading strategy, traders must consider multiple parameters. Those will be different for short-, mid-, and long-term traders.
The use of a combined approach with timely pivots brings the best results.
There is a natural tradeoff between simplicity vs. profit margins. Every simple strategy will be limited. So, too, the profits.
This is why an automated trading system needs to include trading suites, i.e., offer end users a selection from several strategies and dozens of parameters. This way, flexible automation tools become critical when following technical indicators and/or executing orders. As outlined in our algorithmic trading software development guide, flexible automation tools become critical when following technical indicators and/or executing orders.
Trading platforms make it possible to:
- set emotions aside
- increase entry speed
- apply several strategies to the trading process
One thing must always remain in focus: trading software is only a tool. Users still need to check activities regularly. Why? Every system has blind spots and might misinterpret anomalies. It might miss a change of trend direction. The result always ends in losses.
Also, markets never stand still. Any winning strategy might degrade over time, requiring constant adjustment to evolving conditions.
Therefore, “set it-and-forget it” does not work unless applied to a dollar-cost-averaging strategy.
How to Create Automated Trading Software
Creating trading software has requirements that go beyond writing code: it has to be implemented through efficient algorithms and rapid processing of market information while maintaining proper security standards.
Because this mix of finance expertise, data science, and engineering is hard to cover internally, most companies choose to partner with an experienced trading development team to design, test, and launch a stable, compliant trading solution that performs reliably under real-market conditions.
How to Hire a Company for Automated Trading Software Development
1. Define your goals
Clarify what you want to achieve – faster execution, fully automated strategies, better analytics, or improved risk control. Clear goals shape accurate technical requirements.
2. Check trading expertise
Look for a team with real experience in trading platforms, market data integration, and algorithmic strategies. Domain expertise directly affects software quality.
3. Review case studies
Study the company’s previous projects to see the complexity they can handle and whether they’ve built similar trading or fintech solutions before.
4. Assess tech stack
Make sure the team works with technologies suitable for low-latency processing, market-data streaming, cloud deployment, and secure architecture. The right tech stack defines performance.
5. Discuss compliance
Trading software must meet strict security and regulatory standards. Ask how the company handles encryption, audits, logging, and compliance requirements.
6. Start with an MVP
Begin with a minimum viable product to validate your idea with real market conditions. This reduces risks and lets you scale features gradually.
Top Automated Trading Software Development Companies
1. IT Craft
IT Craft offers trading software development services and helps clients understand how to build powerful, secure trading software that supports automated strategies and high-performance execution.
The company develops secure, high-performance solutions for fast execution, real-time analytics, automated strategies, and seamless integration with both crypto and traditional markets. IT Craft’s teams operate under strict regulatory and security requirements to ensure every product performs reliably in live-market environments.
- Services & expertise: Сustom trading & investment platforms, custom trading software development, automated trading strategies and trade bots, market-data integration and streaming, crypto exchange & wallet features, platform modernization and performance optimization
- Technology stack: .NET, Node.js, Java, Python, React, Angular, Vue, SQL/NoSQL, AWS, Azure, WebSockets
- Team size: 330+ experts
- Top Clients: LimpitMarket, Predira
Need an automated trading platform or custom trade bot?
Contact IT Craft to discuss your automated trading software requirements.
Contact
2. Quantovate
Quantovate is an automated trading software development company focused on building custom strategies and tools on NinjaTrader. They specialize in production-grade automated strategies engineered for precision, robustness, and live trading.
- Services & expertise: Custom automated trading strategies for NinjaTrader, StrategyCore / QVCore-based frameworks, semi-automated and fully automated execution logic, backtesting/optimization/live deployment, ongoing strategy maintenance
- Technology stack: C#, .NET, market data APIs, broker integrations, cloud tooling
- Team size: 9 experts
- Top Clients: Independent traders, small trading firms, trading educators
3. Biz4Group LLC
Biz4Group LLC builds custom trading platforms and financial analytics solutions for companies that want to modernize their digital trading experience. Their work spans multi-asset trading interfaces, mobile and web trading applications, cloud-native infrastructure, and AI-enhanced analytics modules.
The company combines enterprise-grade engineering with a strong product approach, helping teams launch MVPs, automate investment workflows, and integrate with brokers, KYC/AML providers, and payment systems.
- Services & expertise: Custom stock and multi-asset trading platforms, trading platform MVPs, real-time charts/quotes/order management, AI/ML-powered analytics, broker/KYC/AML/payment integrations
- Technology stack: Java, Node.js, Python, React, Angular, iOS/Android, AWS, GCP
- Team size: 200+ experts
- Top Clients: Walmart, FanFuel, Legacy Concierge
4. Suffescom
Suffescom specializes in fintech and crypto trading platforms, combining automated trading logic with blockchain-driven features. The company builds everything from white-label crypto exchanges to AI-enhanced futures platforms, trading journals, liquidity modules, and analytics dashboards.
Their engineering team focuses on high-performance, scalable architectures that support rapid order execution and large volumes of real-time data, which is especially important for crypto trading environments.
- Services & expertise: White-label crypto exchange development, AI-powered trading journals, AI-driven crypto futures platforms, high-frequency trading support, real-time analytics dashboards
- Technology stack: Node.js, Java, Python, Solidity, React, AWS, MongoDB, microservices
- Team size: 150–200 experts
- Top Clients: RealEx, Sportzchain, Fanfare Global, multiple NDA-protected crypto exchanges
5. PixelBrainy
PixelBrainy is a boutique design and engineering studio focused on modern trading interfaces and AI-powered trading agents. Rather than trying to cover the entire fintech spectrum, the company specializes in user experience, front-end development, and experimental AI tools that help traders act faster and more confidently.
Their projects often include intelligent bots, multi-device trading experiences, streamlined real-time interfaces, and early discovery or MVP work for fintech founders who need design-heavy, product-centric support.
- Services & expertise: Trading platform UX/UI, AI trading agent and bot development, real-time trading interfaces, multi-device trading experiences, fintech discovery/PoC/MVP work
- Technology stack: React, React Native, backend APIs, cloud infrastructure, AI toolkits
- Team size: 30–60 experts
- Top Clients: Focused Trading App, ProSkill, Rathore FMCG, several NDA fintech startups
6. Itransition
Itransition is a large enterprise-focused software development company with extensive experience in trading, capital markets, and investment software. They build scalable trading platforms, algorithmic trading engines, portfolio management systems, analytics/BI solutions, and full-scale digital asset platforms.
With thousands of engineers and a global delivery model, the company works with both financial institutions and fast-growing fintech companies that require strong architecture, compliance, and long-term system support.
- Services & expertise: Stock and multi-channel trading platforms, automated trading algorithms, portfolio/risk management tools, crypto trading & exchange platforms, financial analytics & BI systems
- Technology stack: Java, .NET, Python, C++, modern front-end frameworks, AI/ML, AWS, Azure
- Team size: 3000+ experts
- Top Clients: TradeSmith, Tectrade, financial institutions (NDA)
7. EffectiveSoft
EffectiveSoft is a custom fintech software development company that helps clients transform trading ideas into reliable digital products – from standalone automated algorithms to full trading platforms with data feeds, risk tools, and advanced UI/UX. They work with both traditional markets and crypto, supporting teams that need technical validation, PoC development, or full-cycle engineering.
Their developers often collaborate closely with quants, traders, and financial analysts to translate trading logic into software that performs consistently in live market conditions.
- Services & expertise: Automated trading software (strategy→algo→bot), real-time trading platforms & mobile apps, FIX/broker integrations, market data processing & analytics, risk and portfolio management tools
- Technology stack: .NET, Java, Python, SQL/NoSQL, iOS/Android, AWS, GCP
- Team size: 350+ experts
- Top Clients: Magma Trading, financial institutions (NDA), brokerage & trading product companies
Summing Up
Scripts and algorithms have long become fundamental trading instruments.
Automation takes trades to the next level. Traders create, backtest, and implement complex, sophisticated strategies with its help. They spot opportunities and enter them at the speed of light.
A great platform supports multiple automated trading strategies making it possible to survive and thrive in an intensified trading environment. At IT Craft, we specialize in custom trading software development, delivering solutions that empower businesses with flexibility, speed, and security.
A great automated trading system provides:
- A suite containing common automation strategies (momentum, day trading, arbitrage, and more).
- Tools for building a specific, niche strategy.
- Analytics tools for monitoring and success measuring.
- Customized dashboard to accommodate needed features.
- Alerts and notifications to detect and eliminate anomalies.
- Top security level ensuring all secrets and know-hows remain safe.
Do you want to improve the trading process but lack the features you need?
We can help. Contact us for a free estimate.
Contact us









