Health Level Seven, commonly known as HL7, is a set of international standards for exchanging, integrating, sharing, and retrieving electronic health information. What is HL7?
It defines the framework for data exchange between healthcare systems, ensuring efficient communication and interoperability.
As healthcare systems continue to digitize, HL7 plays a crucial role in improving the efficiency and interoperability of healthcare technologies. Let’s explore why HL7 remains vital in 2025.
1
What is HL7 in Healthcare?
Health level 7 standards enable electronic health information processing, sharing, and interoperability. With HL7 standards in healthcare, providers can deliver quality patient care more quickly.
The section below describes HL7 and how it secures smooth information flow in healthcare.
Standardized Data Exchange
HL7 standards define the language, structure, and data types that enable seamless exchange in healthcare. With this protocol, the various systems would be able to interpret the data for appropriate usage, leading to many errors and inefficiency.
- Consistency Across Systems: HL7's key role is to provide consistency in data exchange, ensuring that patient information—such as demographics, treatment records, and diagnostic results—can be transferred and understood across different healthcare platforms.
- Application Layer Protocol: The term "Level Seven" refers to the application layer in the OSI, or Open Systems Interconnection, model, which governs data exchange between applications. By focusing on the application layer, HL7 assures that healthcare data are exchanged meaningfully, even across disparate systems.
Reduced Errors and Enhanced Communication
By standardizing how information is exchanged, HL7 becomes clear in healthcare: it plays a crucial role in reducing the risk of errors due to miscommunication between healthcare systems.
- Error Reduction: Systems using different formats might misinterpret data, leading to dangerous medical errors. With HL7, data is always interpreted the same way, helping to reduce misunderstandings and miscommunication.
- Efficient Workflow: From appointment scheduling to laboratory results delivery, HL7 helps develop workflows more efficiently, which means better patient care while reducing healthcare professionals' workload.
Unlock Seamless Interoperability of Healthcare Data
Are you ready to transform healthcare systems into a more interoperable model? Let our experts guide you in implementing the most efficient data exchange solutions using HL7.
Get started today!
2
What are HL7 Standards?
HL7 has evolved several versions to meet healthcare data’s growing demands and complexities. The HL7 meaning in healthcare is significant because it ensures that different systems can exchange and interpret data reliably, improving patient care and operational efficiency.

HL7 v2
Developed in the late 1980s, HL7 v2 is still one of hospitals’ most widely implemented standards worldwide. It primarily handles administrative messaging, such as patient registration and admission details.
HL7 v3
HL7 v3 aimed to improve upon v2 by introducing more complex data structures. Though less commonly adopted than v2, it provided a foundation for future advancements.
HL7 FHIR
FHIR, or Fast Healthcare Interoperability Resources, combines the best features of HL7 v2 and v3, embracing modern web standards to simplify healthcare data exchange faster and more adaptable to new technologies.
HL7 CDA (Clinical Document Architecture)
This standard defines the structure and semantics of clinical documents, facilitating healthcare information exchange in a standardized format that supports interoperability and meaningful use.
HL7 CCD (Continuity of Care Document)
An HL7-compliant standard that provides a comprehensive snapshot of a patient’s health information, supporting the exchange of key data for ongoing care and transitions between healthcare providers.
3
What is an HL7 Interface?
An HL7 interface is a specialized software tool that enables communication between different healthcare information systems using the HL7 (Health Level Seven) standard.
In essence, it serves as a translator, allowing diverse systems such as Electronic Health Records (EHR), Laboratory Information Systems (LIS), and Radiology Information Systems (RIS) to share critical healthcare data seamlessly.
Due to differences in data formats and communication protocols, these systems can exchange information with an HL7 interface.
An HL7 interface plays a key role in streamlining the flow of medical information. For example, when a patient undergoes a lab test, the results must be shared with the healthcare provider’s EHR system.
The interface translates the data generated by the LIS into a format that the EHR can understand, ensuring that the provider receives accurate, real-time information.
This data exchange typically occurs through HL7 messages, structured to clearly convey patient information, diagnostic results, or treatment updates.
4
What is HL7 Integration and Integration Process
The HL7 integration process ensures that various healthcare systems can communicate effectively. It involves setting up and maintaining interfaces that enable data exchange between systems such as EHRs, LIS, RIS, billing systems, and more.
Successful integration streamlines workflows, enhances data accuracy and ensures timely information sharing, which can significantly improve patient care. Here’s a detailed look at the HL7 integration process.
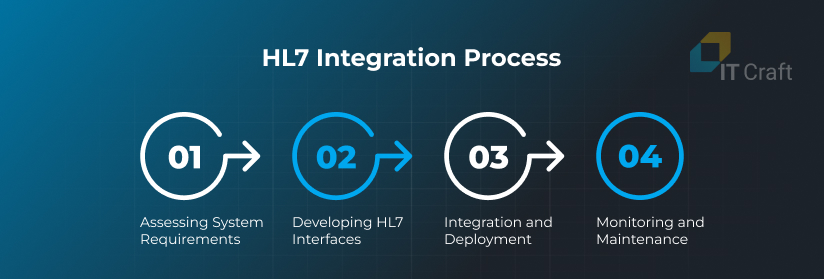
Assessing System Requirements
The first step in HL7 integration is to assess the organization’s needs and identify the systems that require integration. Healthcare institutions often use multiple systems for managing patient records, diagnostic tests, billing, and more. Each of these systems may handle different data formats and communication protocols.
Key considerations include:
- System Compatibility: Determining whether the systems support HL7 standards or require additional configuration.
- Data Exchange Requirements: Identifying the specific types of data (e.g., lab results, patient demographics) that need to be exchanged between systems.
- Versioning: Choosing the appropriate HL7 version (e.g., v2, v3, or FHIR) based on the organization’s technological landscape.
Developing HL7 Interfaces
Once the systems and data flow requirements are identified, the next step is to develop HL7 interfaces. These interfaces enable systems to communicate by formatting the data into HL7 messages that both sending and receiving systems can interpret.
Key steps include:
- Customizing the Interface: Each system may require unique formatting to handle HL7 messages correctly. The interface must be customized to ensure compatibility between systems.
- Message Types: HL7 messages are categorized by their purpose, such as admission, discharge, and transfer (ADT), laboratory orders (ORU), and billing (DFT). The interface must be designed to handle all relevant message types.
- Testing: Rigorous testing ensures the interface can handle data accurately and efficiently without introducing errors. Various scenarios, including normal data exchanges and edge cases, must be tested to guarantee reliability.
Integration and Deployment
After developing the HL7 interfaces, they are integrated into the healthcare systems and deployed into the live environment. This phase ensures that the systems can begin exchanging data in real-time.
Steps in deployment include:
- Pilot Testing: Running a small-scale deployment to monitor the system’s performance and ensure no major issues before a full rollout.
- Data Mapping: Ensuring that data from one system matches the correct fields in the other system during exchanges.
- Security Considerations: During deployment, security protocols such as encryption must be implemented to protect sensitive healthcare information from unauthorized access or breaches.
Monitoring and Maintenance
Once the HL7 interfaces are live, continuous monitoring is essential to ensure smooth operation. This includes tracking message exchanges, identifying potential errors, and optimizing performance over time.
Ongoing tasks include:
- Error Monitoring: Setting up alert systems to catch and resolve errors in real-time to minimize disruptions.
- System Updates: Keeping the interfaces updated to align with changes in healthcare standards or technological advancements.
- Performance Optimization: Ensuring the interface operates at peak efficiency, minimizing delays in data exchanges.
Challenges in HL7 Integration
While the integration process brings significant benefits, it’s not without challenges. Some of the common obstacles include:
- System Compatibility: Legacy systems may only partially support modern HL7 standards, requiring complex configurations or middleware to bridge the gap.
- Data Security: Ensuring data integrity and security during transfers is crucial, as healthcare information is highly sensitive.
- Versioning Issues: Different systems may use HL7 versions (e.g., v2 vs. FHIR), necessitating careful configuration to ensure compatibility.
Transform Your Healthcare Data Systems
Don’t let outdated systems hold you back. Discover how HL7 standards can revolutionize your data exchange.
Explore Our Services Now!
5
HL7 in Healthcare
Health Level Seven (HL7) is pivotal in modern healthcare, serving as the standard for exchanging electronic health information. As healthcare becomes more digitized, the need for standardized protocols to facilitate seamless data exchange has never been more critical.
HL7 provides the infrastructure for diverse healthcare systems to communicate effectively, ensuring patient data is shared accurately and in real time.
The primary goal of HL7 in healthcare is to enable the interoperability of healthcare systems, which can be challenging due to the variety of software platforms used in hospitals, clinics, laboratories, and other healthcare organizations.
These systems manage everything from patient admissions and billing to laboratory results and radiological images.
With standardized communication, these systems could share critical patient information, resulting in inefficiencies, delays, and even errors in care delivery. HL7 helps bridge these gaps, making sure data flows seamlessly between systems. It’s a key enabler of healthcare digital transformation, helping providers deliver faster, safer, and more coordinated care.
Key Areas Where HL7 Is Used in Healthcare
HL7 is integrated into various areas of healthcare to support a wide range of functions. Some of the most common places where HL7 is applied include:
- Electronic Health Records (EHR): HL7 is essential in maintaining and exchanging patient health records between providers. Whether a patient is visiting a primary care physician, specialist, or hospital, their medical history can be shared instantly via HL7-compliant systems.
This ensures that all healthcare providers have access to up-to-date and accurate information, which is critical for effective care. - Laboratory Information Systems (LIS): Lab results are one of the most commonly exchanged types of healthcare data. HL7 enables laboratory systems to communicate test orders, results, and diagnostics to other healthcare providers in a standardized format.
This streamlines the process of requesting and receiving lab results, reducing turnaround times and minimizing the risk of errors. - Radiology Information Systems (RIS): HL7 allows radiology departments to share imaging orders, reports, and results with other systems, such as EHRs. For example, a physician can order an X-ray or MRI through an EHR system, and the radiology department can send the results back using HL7 standards.
This speeds up the process and ensures that all relevant data is documented in the patient's record. - Billing and Financial Systems: Beyond clinical data, HL7 is also used to manage administrative and financial information in healthcare. Billing codes, insurance claims, and other economic data are exchanged through HL7 to streamline the payment and reimbursement process.
This integration ensures that billing information is consistent across all systems, reducing the likelihood of disputes and errors.
6
Benefits of HL7
HL7 offers numerous benefits to healthcare organizations by enhancing how medical information is shared, improving patient outcomes, and streamlining operational processes. Below are some of the key benefits of adopting HL7:

Enhanced Interoperability
HL7 provides a standardized framework that allows different healthcare systems to communicate effectively. This interoperability ensures that data is shared across systems seamlessly, eliminating the need for manual data entry or transcription.
By enabling systems to “speak the same language,” HL7 reduces miscommunications and ensures that healthcare providers can access complete and accurate patient information.
Improved Patient Care
One of the most significant benefits of HL7 is its positive impact on patient care. When healthcare providers can access patients’ complete medical history, lab results, and diagnostic reports in real time, they can make more informed decisions.
This leads to faster diagnoses, more accurate treatments, and improved patient outcomes.
For example, a patient’s lab results can be immediately shared with their physician, enabling quicker response times and reducing the need for follow-up visits.
Reduced Administrative Burden
By automating healthcare data exchange, HL7 significantly reduces the administrative burden on healthcare staff.
Previously, medical professionals had to manually enter or transfer data between systems, which was time-consuming and prone to errors. HL7 eliminates these inefficiencies by ensuring that data is shared automatically between systems, freeing up staff to focus more on patient care.
Cost Savings
Automating data exchange through HL7 can lead to substantial cost savings for healthcare organizations. By reducing the need for manual data entry and minimizing the risk of errors, organizations can save time and resources.
Additionally, faster access to accurate data can lead to better clinical outcomes, reducing the need for expensive treatments or hospital readmissions.
Better Compliance with Healthcare Regulations
HL7 ensures that healthcare data is exchanged and standardized securely, making it easier for organizations to comply with regulations like the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA).
It also simplifies audits and reporting processes, ensuring that all data follows a consistent format.
7
What is the Difference Between HL7 and FHIR?
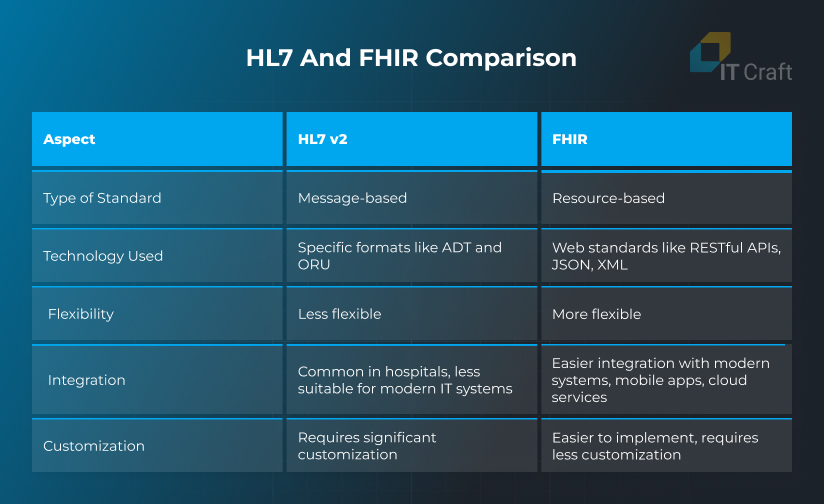
HL7 and FHIR are both standards for healthcare data exchange, but they differ in how they operate. HL7, widely used since the 1980s, is message-based and relies on specific formats like ADT and ORU for data sharing.
While it’s still common in hospitals, HL7 v2 is less flexible and requires significant customization.
FHIR, on the other hand, is a modern standard that uses web-friendly technologies like RESTful APIs, JSON, and XML. It is resource-based, meaning data is broken into smaller, modular elements called resources, which makes it easier to integrate with newer systems, mobile apps, and cloud services.
Key Differences:
- HL7 v2 is message-based; FHIR is resource-based.
- FHIR uses web standards, making integrating with modern IT systems easier.
- HL7 v2 requires more customization, while FHIR is more flexible and easier to implement.
In summary, while HL7 v2 remains relevant, FHIR is the future of healthcare data exchange due to its modern architecture and scalability.
8
How Can IT Craft Help with HL7?
IT Craft provides comprehensive HL7 solutions, offering custom interface development, FHIR integration, and migration services to ensure smooth data exchange in healthcare systems.
Services include:
- Custom HL7 Interfaces: Tailored to your organization’s needs, ensuring accurate, real-time data sharing across systems like EHRs, LIS, and RIS.
- FHIR Integration: We implement FHIR for mobile and cloud platforms, enabling seamless interoperability using modern web standards.
- HL7 v2 to FHIR Migration: Smooth transitions from HL7 v2 to FHIR, ensuring data integrity and minimal disruption to operations.
With years of experience, IT Craft helps healthcare providers enhance interoperability, improve patient care, and streamline workflows using HL7 and FHIR standards.
!
Conclusion
Moving into 2025, HL7 remains a backbone framework in health data exchange and has been continuously extended to meet the current needs of health systems.
With standards like HL7 v2, v3, and FHIR, communications between diverse healthcare applications have been made easier and have ensured interoperability for patient care.
As the industry moves further into digital transformation, HL7 will be right at the leading edge in driving data exchange, assuring that providers can securely and proficiently share information across systems to enable quality and coordination of care. This evolution plays a critical role in shaping the future of telehealth and reinforces the need for tailored custom healthcare software development that supports secure, interoperable solutions.












