ERP software for the logistics industry requires time, investment, and in-depth expertise in business.
Still, these crucial three elements might not be enough for success.
As with every fundamental system, building and maintaining an effective ERP system is challenging. According to a McKinsey report, 75% of ERP transformation projects experience fractured deadlines or cost overruns and 67% result in a negative ROI.
A solution exists: use an Agile approach for a profitable ERP system in logistics. Agile teams retain software development in constant alignment with business needs.
1
What is a Logistics Management Platform? Why use ERP?
A logistics management platform maintains effective processes by supporting different elements of a supply chain, e.g., warehousing, fleet, route management. Learn how it contributes to supply chain management optimization and improves overall operational efficiency.
Different implementations exist. Businesses can:
- Use ready-made systems provided by third-party vendors, including:
- Simple solutions that enhance single operations.
- Complex ERP software for the logistics industry.
- Enrich a ready-made suite.
- Build a fully custom system.
In each case, estimated implementation costs of an ERP system are not the only factor. In logistics, flexibility and time for changes matter.
Companies that regularly adjust their system to changing needs and progressing technologies provide customers with fast and transparent deliveries—the key point for a company achieving top of the charts.
How does a Logistics Management Platform Save a Budget?
By using a relevant ERP solution, businesses benefit the most from streamlined processes:
- Resources optimization. Regular optimization enables obtaining the best effectiveness while reallocating saved resources for business growth, e.g., delivering new functionality.
- Automation at scale. The development team shifts routine manual operations (e.g., billing) to machine automation where possible. It saves hundreds of working hours and cuts out the human error problem.
- Increased transparency. Quality and timing become predictable. Users enjoy real-time monitoring and prompt updates.
- Improved workflow. Employees’ efficiency increases. Collaboration between departments improves.
- High security. The engineering team regularly assesses security risks and vulnerabilities, delivering enhancements to discovered weaknesses. Valuable data is safe.

2
ERP Logistic Software Development: From Start to Complete
The introduction of an Agile approach mitigates risks of unpredictable and inconsistent deliveries. An Agile development team responds better to launch, expansion, and modernization challenges.
According to the same McKinsey report, Agile enables a 10% cost reduction by ensuring less rework and a 20% increase in program value.
Business and engineering teams elaborate on goals and challenges together.
Engineers divide the entire scope of ERP software for logistics into digestible chunks. They deliver working functionality in two-week Sprints.
The team gets feedback on the completed work and integrates it within the next Sprints. It switches flexibly to priority tasks.
The progress track becomes simple and transparent.
Consider the points below for building a relevant logistics system:
Project Planning
Project success or failure depends critically on planning quality. This is where logistics businesses benefit from cooperation with a dependent logistics software development company. They keep a foot in each camp—business and technology—by working with experts who know from experience how to apply Agile methodology to a large ERP project.
Alignment is critical. Involved parties must elaborate on project goals, shared vision, and success criteria. Then they set the correct priorities.
A product owner plays a vital role in the development pace. The product owner is authorized for timely final decisions, decreasing delivery time.
Type of Application
According to a Gartner report, 61% of respondents stated technology is the source of competitive advantage.
It is crucial to determine target platforms.
Many logistics platforms are delivered as responsive Web solutions. Web makes it possible to keep up with development costs for a wide software availability.
Cross-platform development is also possible. It saves costs and ensures simultaneous updates on both desktop and mobile devices.
Often, mobile apps are adjusted to bigger tablet screens. Tablets replace desktops inside warehouses and as POS.
Drivers benefit from smartphone apps. Native app development might be required when an app needs access to smartphone hardware, e.g., using a smartphone camera for scanning documents.
Whatever you choose, opt for microservices to achieve optimum flexibility. By 2026, 25% of software vendors are forecasted to transform their software architecture to microservices benefitting from a future-proof technological base.
Main Modules
ERP systems support a wide range of business processes. ERP modules are autonomous. The development team integrates modules with the central database to ensure accurate data synchronization across all departments, e.g., sales can see stock availability in real-time. Still, they do not affect the processes of the warehouse. They work from a CRM.
The range is wide, affecting implementation costs. Hence, deciding on the most important modules and scheduling the rest later is essential.
The list of ERP modules includes:
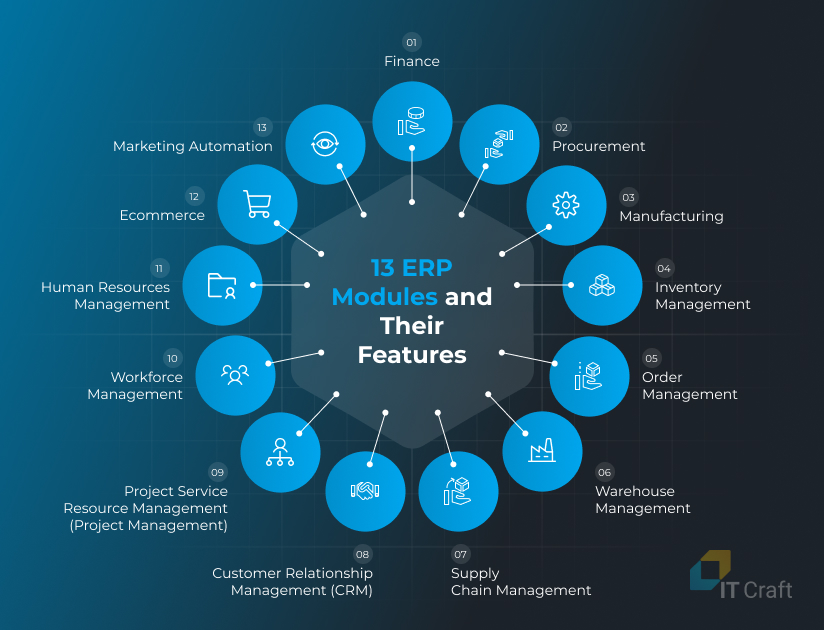
Must-Have Functions
Feature list varies for different modules. Each module can be autonomous and realized as an alone-standing app.
Still, the basic app structure remains common. It includes:
- Login and password recovery
- User profile
- Application menu
- User board
- Management functionality
- Alerts and notifications
- Digital documentation
- History
- Help center
An administration panel is used to monitor the system and its users. Core functionality includes:
- User management
- Password and recovery management
- System settings
- Activities monitoring
- System alerts
- Logging
Data Control
Businesses should decide on IT infrastructure. It can be an on-premises infrastructure that stores and processes data locally. An on-premises data center provides complete control over operations, enhanced data security, and control over hardware.
Still, optimization possibilities are limited for on-premises infrastructure. Cloud infrastructure offers immediate scalability and improved control over expenses. Distributed teams working from distant locations have improved access to the required data. Enhanced security is also a part of cloud services.
API Integration and Management
An API allows data exchange with specialized third-party services, e.g., payments, billing, accounting, and more. By integrating third-party APIs, the development team decreases the timeline. The software receives a competitive edge.
Still, risks exist. Businesses might bump into an increase in variable costs. By paying regular subscription fees based on an accepted pricing plan, they might experience a drastic variable cost increase after reaching a specified amount of provided services.
It is critical to choose a provider and a plan wisely.
Also, when your partners need to exchange data with your software, you might need to consider API development to decrease the load on your system.
Are you thinking of the best-fit solution for your needs?
Contact us to discuss implementation opportunities.
Contact us
3
ERP Logistics Management Platform: Key Features and Benefits
The following features increase the bottom line of ERP software for logistics:
- Delivery updates. The software sends notifications to customers as soon as it automatically detects changes or company workers update information.
- Route planner. The system determines the optimum path depending on the truckload and the number of stops. It ensures the best fuel consumption and working hours.
- Custom calculators. Custom, adjustable calculators are required when a company pursues a flexible yet transparent pricing policy.
- Documents and templates. A large base of available templates is used to generate documents, receipts, billing, etc., simplifying workload.
- Insights and analytics. The development team defines the functionality needed to make sense of a business’s daily data.
- Access management. Access management is critical for fast response to role changes. Only authorized employees access the information they need for work.

4
IT Craft Expertise
MyCarrier
This large transportation management system once started as a web portal where customers requiring less-than-truck-shipments met service providers.
The service became highly popular because it offered direct integration, control over logistics processes, and complete transparency.
Software underwent a large transformation. The development team divided the monolith codebase into microservices and transmitted it to the cloud. The result was increased stability, availability, and scalability.
To see how companies approach such transformations, read the article on custom transportation software and explore how custom development supports long-term growth and operational control.

eLaundry
This CRM was envisaged to simplify customer access to laundry services and improve related processes.
The team later reworked the system to focus specifically on B2B needs.
The software core is data processing. The system monitors and techniques over a hundred metrics to ensure cost-effectiveness.
Automation at scale helps coordinate team efforts throughout the entire laundry cycle. Similar to how logistics automation software streamlines complex workflows in supply chain environments, this solution brings efficiency and visibility to every stage of the laundry process.

!
Conclusion
An ERP platform has become one of the most valuable assets in the constantly digitalized world.
As a business, whatever path you choose, you need:
- building and implementing a new solution from scratch
- upgrades and modernization of your current system
- integration of new features or specific third-party services
- optimization and software transformation
Every change in an ERP system is challenging. You need to be flexible with your goals and priorities. You need to use Agile to be agile.
Make the use of value-driven development and an iterative approach to deliveries a part of your initial plan.
Engage top experts in logistics software development solutions who know how to apply Agile practices to your processes.
This way, you ensure the delivery of relevant functionality faster and with improved quality.








