Telemedicine is one of the best-funded segments in custom healthcare software development due to its vital role in healthcare digital transformation.
According to Data Bridge Market Research, the estimated size of the global telehealth market is $151M. It is growing at a 13.88% CAGR and is predicted to reach $290M by 2028.
Still, interest in the market does not guarantee success for everyone. Telemedicine startups operate in a highly competitive environment. Timely adjustment to the changing landscape is required to meet user expectations, raise funding, and reach profitability and resilience.
Below is IT Craft’s overview of telemedicine trends and technologies that are defining the industry today.
1
Key Insights on Telemedicine Market Trends and Statistics
The future of the telemedicine market looks optimistic, with signs of steady growth. But the market is still far from reaching its full potential and achieving maturity.
- teletherapy and behavioral health,
- care coordination and navigation.
- Three factors account for the high CAGR in data and technology-focused healthcare segments:
1) growing demand for improved efficiency and addressing labor challenges,
2) willingness to absorb increased prices where value is clear,
3) increased operational efficiency through technologies and automation.
- Three main goals of telehealth are improved access to healthcare services for vulnerable patients, reimbursement parity for service providers, and effective application of telehealth solutions.
- Cancer patients can save on average between $147.40 and $186.10 per visit in indirect costs with telehealth appointments.
- 25% of US patients used telehealth services in 2022, compared to 5% pre-pandemic, according to the American Medical Association.
- According to a SingleCare report, US adults are most willing to use telehealth apps for consultations on common illnesses/infections (69%) and follow-up visits (66%).
- Estimated telemedicine app development costs vary between $56,000 and $700,000, while the development timeline starts at 2,800 hours to plan, develop, test, and launch a telehealth system. The actual cost depends on a team’s location and level of expertise. With an experienced team from a cost-effective location, you can stay at the lower end of this range.
- The annual cost of software maintenance is typically 10% to 15% of the initial development cost.
Although it takes longer for healthcare companies to achieve significant ROI compared to other companies offering SaaS products, HealthTech companies show strong public and private market performance and can scale with profit. Healthcare SaaS companies have seen 3.1× ROI on average over the last decade, while healthcare services businesses attain 2.6× ROI on average.
2
Current Telemedicine Trends
Telemedicine solutions remain in high demand. Specific market trends focus on meeting changing user habits and socioeconomic disruptions:
mHealth
In 2024, portability is emerging as a pressing concern among service providers as end users — doctors and patients — are widely choosing to access telehealth systems from smartphones and tablets. Any telehealth solution is a complex system consisting of:
- a web administration panel,
- mobile apps for iOS and Android,
- a web interface for desktops/laptops,
- a back end, and
- connected devices.
Seamless data exchange between parts of the system via APIs is critical to ensure convenience of patient-doctor interactions.
Preventive Care
Concern for end-users’ well-being is one of the most important telehealth trends. For instance, healthcare industry professionals can encourage proper nutrition and physical exercise by creating fitness apps.
Social networking and gamification features increase accountability and adherence to healthy habits. Mental health apps are another big trend in telehealth.
Burnout Prevention
Telehealth solutions are also aimed at improving clinical staff’s well-being. They can reduce staff burnout and overload — two major factors in the medical labor shortage.
Automation, virtual nursing, and elimination of unmonetized calls outside working hours also help to prevent burnout.
UX Improvement
Building an intuitive telehealth app is a daunting task due to the complex nature of such apps and the multiple laws and regulations with which they must comply.
Nevertheless, a telehealth app should require as little training as possible on the part of medical professionals and patients. Numerous user studies are needed to eliminate adoption barriers.
Increased Competition
Another consequence of the wide adoption of telehealth solutions is skyrocketing competition between service providers.
Similar to how customers of brick-and-mortar stores can shop online from the comfort of their homes, patients can now quickly reach telehealth providers even in remote areas, increasing providers’ reach and ability to compete.
Market Consolidation
Startup acquisitions by big companies were common in 2022 and 2023 and will continue to be a trend in 2024. Industry experts consider mergers and acquisitions a natural path for telehealth startups due to high interest rates, market slowdowns, and growing interest in full-fledged solutions.
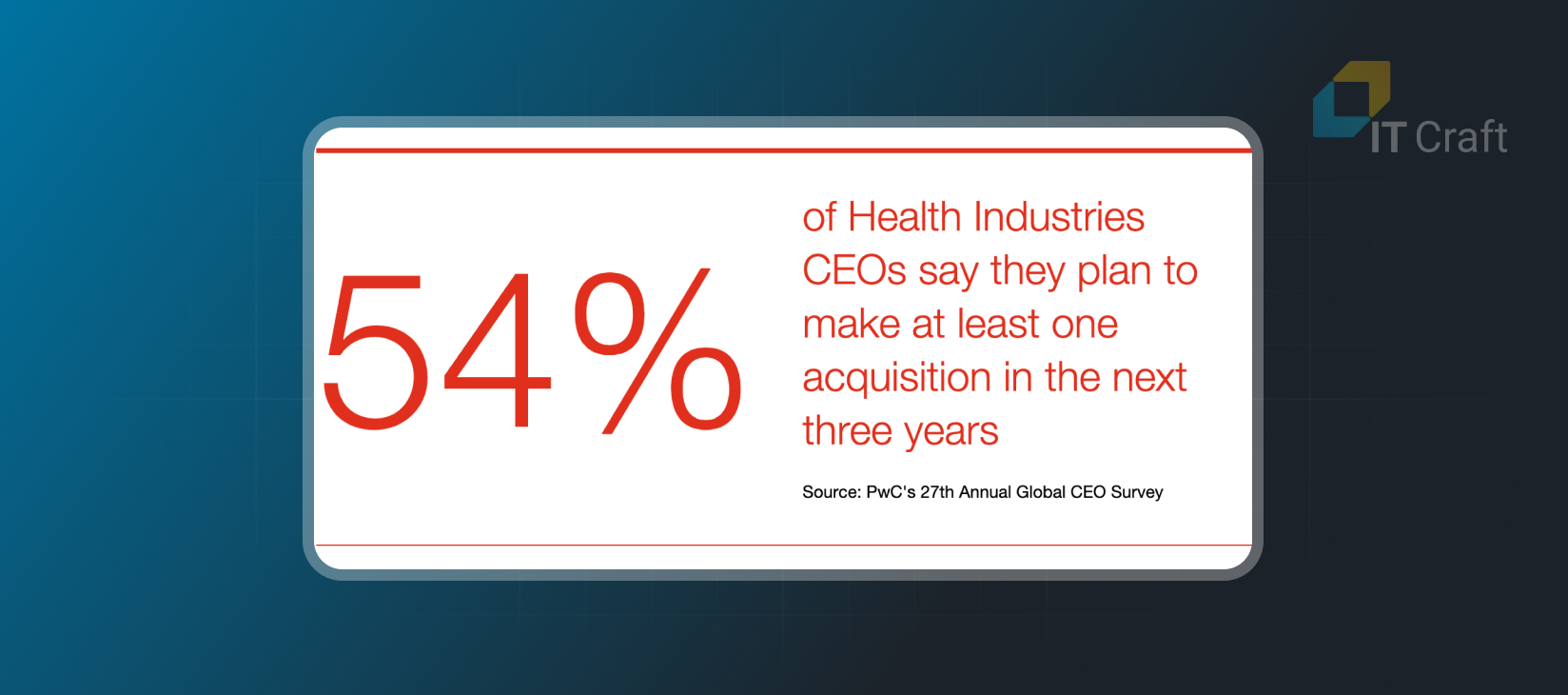
Source: PwC’s 2024 Outlook on Global M&A Trends in Health Industries
Small and midsize startups are forecasted to exit in 2024. Those who do not will seek consolidations and partnerships needed to create robust platforms. The reason: users prefer a unified workflow. Managing several apps from different vendors can be tiresome.
3
Future Telemedicine Technology Trends
Let’s take a closer look at telemedicine trends and technologies that will grow in importance throughout 2024, helping eliminate bottlenecks and inefficiencies.

Generative AI
Generative AI is an emerging trend. It lets healthcare professionals structure and summarize data, provide notes and instructions, create checklists, and more. All in natural language.
Tight cooperation and knowledge sharing between software developers and healthcare professionals is key to launching and calibrating a generative AI system, while its accuracy relies heavily on accumulated industry expertise. This means that doctors and nurses must participate in AI development projects and understand to at least some extent how AI works.
Remote Patient Monitoring (RPM)
RPM helps to efficiently manage patients’ acute and chronic conditions. With RPM, patients save money they would otherwise spend on trips to hospitals. In turn, clinics can optimize their administrative workload, decrease no-show rates, and efficiently monitor patients.
Trends in RPM include integrating telehealth software and monitoring systems into a comprehensive platform, emphasizing a holistic view of patient needs, focusing on predictive analytics, and increasing equality of access to healthcare services.
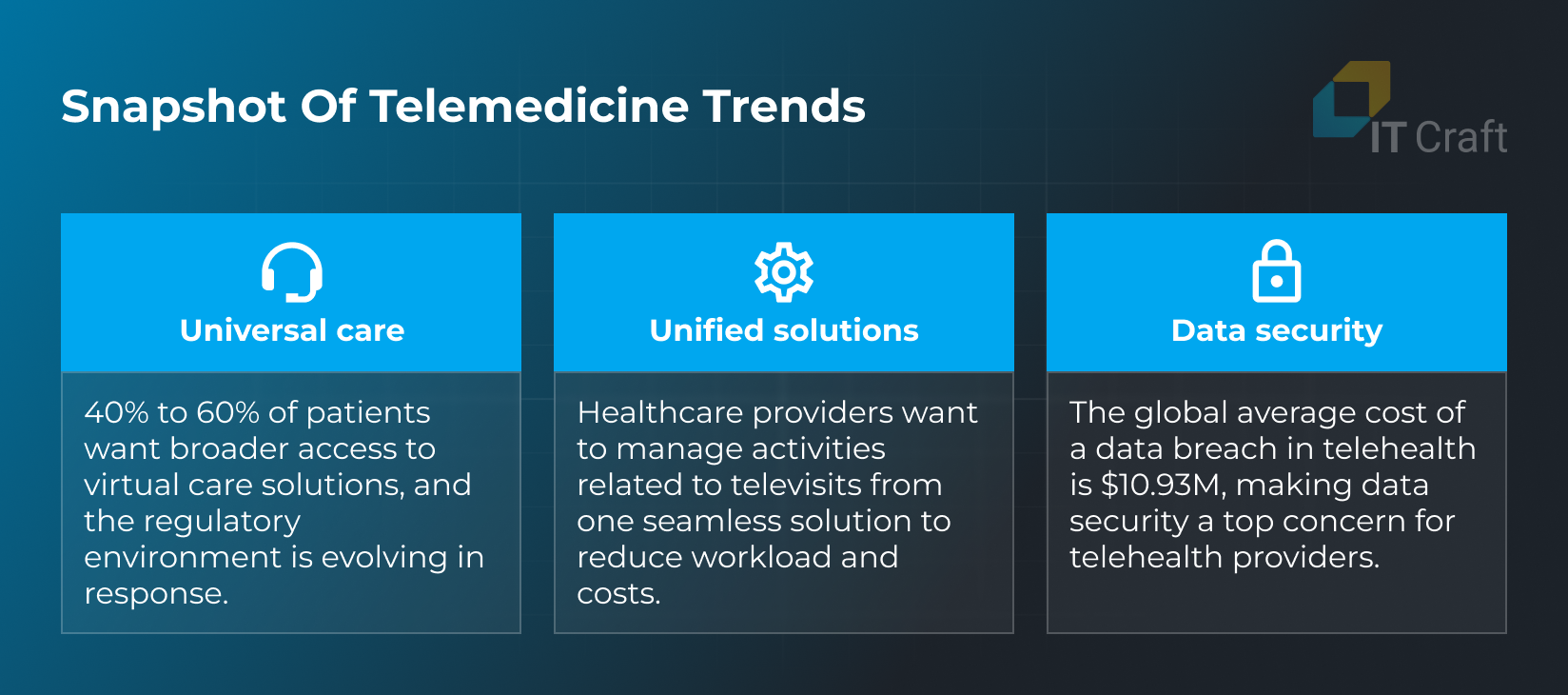
Universal Care
Medical policies continue to evolve, ensuring greater flexibility in providing and accessing services.
A crucial result of improved telehealth coverage and reimbursement is greater access to telehealth services among patients and the ability to provide teleservices for providers. All institutions that are eligible to bill Medicare can bill for telehealth.
Private insurance plans, too, have started including telehealth coverage.
Data Security
Security concerns will only increase with telehealth adoption. Medical devices collect, store, and transmit valuable information about their owners, and a single data breach in healthcare cost $10.93M on average in 2023.
Telehealth presents complex security challenges since cybercriminals of all kinds are highly interested in breaking telehealth systems and related infrastructure. Manufacturers and software developers need to ensure a high level of security while maintaining user comfort.
Meanwhile, healthcare providers must educate personnel and patients on the basics of safely handling medical devices.
EHR-embedded Telecare
Electronic health record (EHR)-embedded telemedicine is a key step in healthcare digital transformation. EHR solutions greatly improve a clinic’s workflow, allowing patients to make and manage appointments in a few clicks.
Doctors document medical information directly in an EHR system. Medical institutions can use EHRs to avoid duplication of information and related errors caused by unintegrated software suites.
IoT and IoMT
The Internet of Medical Things (IoMT) includes sensors, infrastructure, and related software solutions. The four key categories of IoMT devices are in-home, on-body, community, and in-hospital.
IoMT provides immense benefits: Goldman Sachs estimates that IoMT devices could save healthcare providers up to $300B annually as a result of fewer adverse events, optimized service costs, improved productivity, and increased capacity of healthcare services.
AR and VR
AR apps improve learning outcomes for doctors, nurses, and other medical professionals. Therapists can use AR technology to explain bodily processes to patients and visualize the results of medical tests.
Virtual reality is already used to create a safe environment when treating mental trauma. It can also be used to hold medical consultations with remote patients. Active VR is the next step in physical rehabilitation.
4
Pros and Cons of Telehealth Adoption
The good news is that the pros of telemedicine outweigh its cons. Telehealth is a worthwhile investment for large clinics, midsize private providers, and even individual practitioners.
Pros of Telehealth
Here is how single actors in the healthcare industry win with the wide adoption of healthcare trends:
No-show rates are significantly lower for telehealth appointments than for face-to-face visits.
With telehealth, doctors can distribute their time more efficiently. Waste is minimized, and patients can save time and money on trips to medical facilities.
- Improved treatment efficiency
Telehealth shortens wait times for medical consultations. Patients can use telehealth services to connect with medical providers flexibly for faster responses to specific questions.
Using telehealth services and IoMT, on-duty doctors can receive notifications when a patient’s vitals change and either alert responsible staff or take action immediately.
Telehealth offers people in remote areas an alternative to driving long distances. In turn, medical practices benefit from a wider patient base by implementing a telehealth system.
- Reduced risk of infection
Telemedicine means patients and clinic personnel are less exposed to pathogens, which particularly benefits patients with compromised immunity.
In addition to the advantages, keep in mind limitations and challenges of implementing telehealth solutions:
Disadvantages of Telehealth
The patient base may not be tech-savvy. A telehealth solution must provide a straightforward UX, requiring little training. Every step needs to be transparent and easy.
Telemedicine cannot replace all face-to-face visits. Some examinations, such as blood tests, are available only in clinics. Also, holding a child’s attention during a televisit can be difficult.
Telehealth platforms are expensive to build and implement. The investments required for creating a telehealth solution can be too high for a single clinic. Additionally, patients and insurance companies may be worried about equipment costs and therefore refuse to use telecare services.
Telemedicine startups must keep in mind that scaling can be difficult. Specific regulations apply to different markets, requiring investment in compliance when startups try to reach new users. Understanding how HL7 is used in healthcare can help teams navigate interoperability requirements and build solutions that meet industry standards.
5
COVID-19 Impact on the Telehealth Market
The COVID-19 pandemic catalyzed wide — and urgent — adoption of telehealth for patient consultations, making access to medical examinations as safe as possible.
One of the key drivers of the increased number of telehealth appointments in the US during the pandemic was the lifting of use restrictions and ensured payment parity. During the COVID-19 pandemic, healthcare providers received the same reimbursement for telehealth services as for in-person visits.
For instance, the number of telemedicine services provided under Medicare increased from 5 million between April and December 2019 to 53 million for the same period in 2020.
According to Statista, 65% of US physicians did not use telehealth solutions before the COVID-19 pandemic, while 43% were heavy users at the pandemic’s peak. Also, 43% of physicians plan to continue using telehealth services post-pandemic for up to half of their appointments.
6
IT Craft’s Take on Adopting Telemedicine Trends and Technologies
IT Craft helps startups launch and maintain secure digital platforms for the healthcare industry.
Below are examples of digital healthcare solutions for startups that have worked well for different stakeholders:
XPERTyme
XPERTyme is a web platform for secure video communication that enables professionals to organize calls with industry experts while streamlining administrative work.
A special telehealth platform, MEDITyme, is part of the expanded XPERTyme ecosystem. Clinics use MEDITyme as a scalable white-label solution to enable their custom communication platform to manage televisits.

Arctrieval Legal
This HIPAA-compliant web app streamlines correspondence between medical institutions and legal representatives.
Arctrieval supports the complete patient request lifecycle, processing all sensitive data in an encrypted way. Inquiries and follow-up notifications are automated.
The system also provides a secure workflow for sending paper communication.

!
Conclusion
The telehealth services market is poised to prosper and mature in 2024, with technological improvements, growing demand for teleservices among patients, and a desire to optimize among service providers being the major drivers.
When legislation allows, healthcare software development can be Agile and flexible, quickly meeting changing market needs.
Timely adoption of emerging technologies is critical to offer competitive telehealth services. Telehealth products require strong engineering talents experienced in navigating telemedicine technology trends.
This is why you should work with a team who knows how to avoid pitfalls while delivering a secure solution that both meets patients’ needs and complies with industry regulations. Partnering with experts in healthcare software development services ensures your product is built with scalability, compliance, and user experience in mind.







