Keep your finger on the pulse of the IT industry. You will be aware that the most upbeat trends are mobile indoor navigation technologies and the massive amounts of data those technologies help collect and manage.
The market for indoor location services is expected to expand from $10.9 billion in 2023 to $29.8 billion by 2028, experiencing a Compound Annual Growth Rate (CAGR) of 22.3% over the forecast period. Implementing wireless technologies inside brick-and-mortar stores also creates value for customers as it helps them orient themselves, make choices, and pay most conveniently.
The following three steps will help you become aware of the obstacles that await you when you deploy your wireless indoor navigation system and show you how to avoid or at least minimize their impact.
What is an indoor positioning system?
An Indoor Positioning System (IPS) is a sophisticated technology for tracking people and assets within buildings. It employs a network of devices communicating with sensors distributed throughout the interior space.
Here’s how it works and what technologies are involved:
- Data Processing: Sensor-acquired data is sent to backend software or an application.
- Algorithmic Location Calculation: The software uses mathematical algorithms to pinpoint the object's indoor location.
- Diverse IoT Technology Stacks: Depending on goals and requirements, various technologies are used, including:
- Wi-Fi
- UWB (Ultra-Wideband)
- RFID
- BLE
- Additional Technologies: While the above are primary, other IPS technologies exist.
IPS technologies are gaining momentum across sectors where location-based services are vital. They benefit both building owners and users, offering streamlined experiences.
Key aspects include:
Businesses gain a competitive edge by enhancing user navigation experience.
- User-Friendly Applications:
Users can navigate spaces in real-time and find specific destinations via app-based maps.
- Revenue and Management Improvement:
IPS can open new business revenue channels and improve facility management.
2
Types Of Indoor Tracking Technology
Indoor tracking technology encompasses various systems, each with its distinct features and applications. These indoor positioning technologies are crucial in navigating complex indoor environments, enhancing operational efficiency, and improving user experiences.
Below, we delve into five key types of indoor tracking technology, exploring their unique mechanisms and applications.

Proximity-Based Technology
Proximity-based technology is essential for determining the general location of people or objects within a facility, typically to the nearest room. This is different from precision systems like ultra-wideband, which pinpoint exact coordinates.
- Types of Proximity-Based Systems
Reader-Based Systems:
- Utilize simple, cost-effective tags, often called “dumb” tags.
- Tags broadcast their ID to multiple readers.
- The backend system calculates the position based on tag IDs and signal strength.
Reference Point-Based Systems:
- Known for being more cost-effective within proximity solutions.
- Require fewer readers due to low-cost reference points.
- Offer extended battery life and more accurate location data than reader-based systems.
Applications and Recommendations
- Both systems are widely used in healthcare, manufacturing, and other sectors.
- Reference point-based systems are generally more economical.
- Further research is advised for a deeper understanding and to choose the best solution for specific needs.
WiFi-Based Positioning Systems
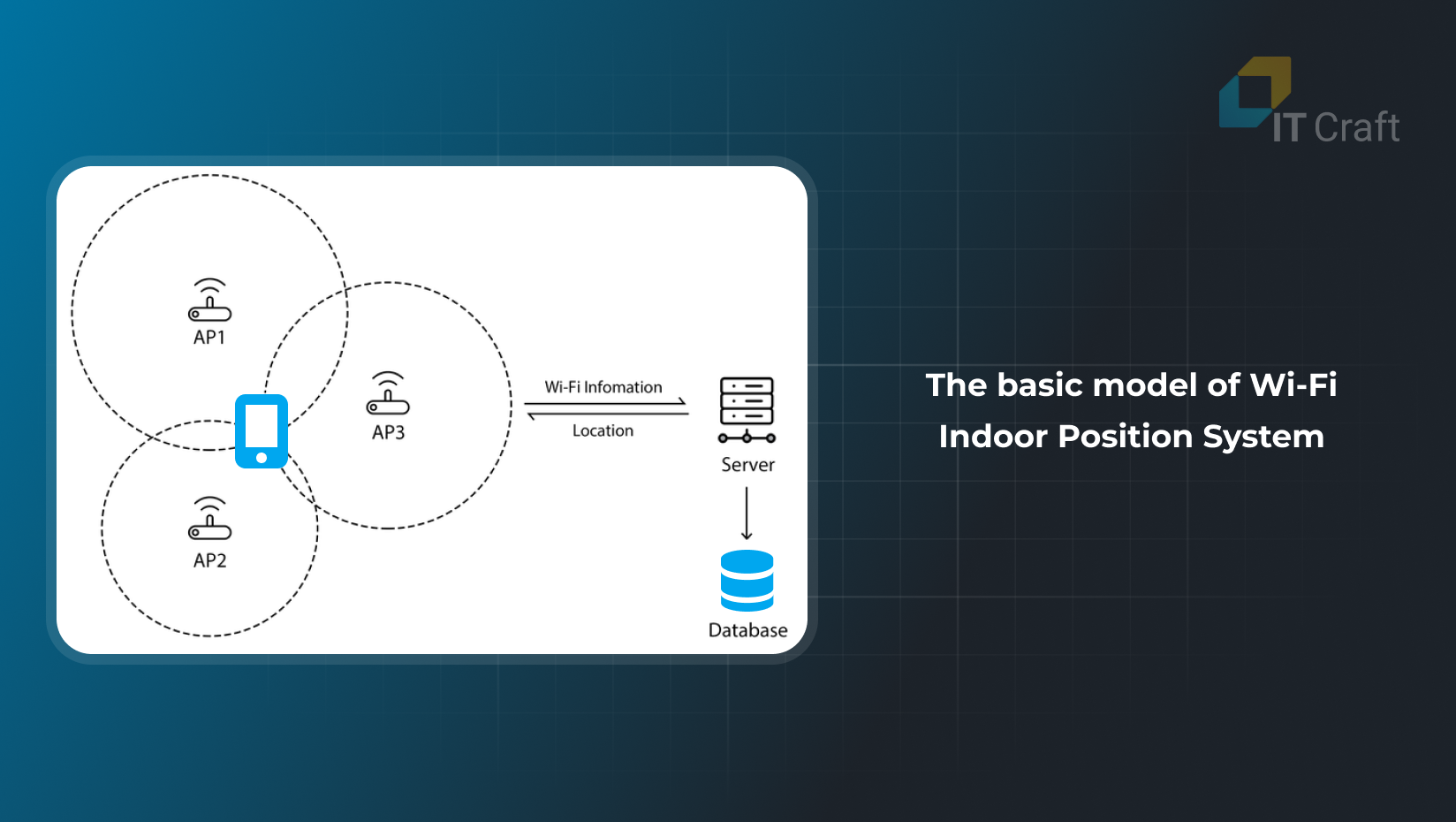
In a WiFi-based high-precision indoor positioning system, tags work as WiFi transmitters, sending data to several access points in a facility. These points record the transmission’s time and signal strength. A central system then processes this data using advanced algorithms to determine the tags’ exact locations stored in cloud-based servers.
WiFi precise indoor positioning systems offer a relatively high level of accuracy, typically within a range of three to five meters. This accuracy is achieved using time difference of arrival (TDOA) measurements with a broad bandwidth.
Key Aspects of WiFi-Based Positioning Systems:
- Tag Functionality: Act as WiFi transmitters, broadcasting data to access points.
- Data Capture: Access points record timestamps and signal strengths of transmissions.
- Position Calculation: A backend system uses advanced algorithms to determine tag locations.
- Data Storage: Location information is stored in cloud-based systems.
Considerations for Implementing WiFi-Based Systems:
- Accuracy Level: Generally within 3 to 5 meters.
- Technical Requirement: At least three access points are needed for optimal accuracy.
- Cost Factors: High cost due to the need for multiple access points and expensive tags ($40 to $60 each).
- Power Consumption: WiFi tags may use more power compared to other types.
Ultra Wide-Band (UWB) Technology

UWB technology is a remarkable innovation. In UWB systems, three or more ultra-wideband readers transmit exceptionally wide pulses across a gigahertz spectrum.
Readers then actively listen for signals, known as chirps, emitted by ultra-wideband tags.
These tags employ a spark-gap-style exciter to generate brief yet powerful pulses, resulting in short, coded bursts of wide-ranging signals.
Subsequently, the readers collect highly precise time measurements from these tags and relay this data to a central server.
The exceptional width of the UWB signal contributes to the system’s remarkable accuracy, making it the most precise positioning technology available.
However, it is essential to acknowledge that UWB installation tends to be the most costly among precise indoor positioning systems. While UWB tags are relatively affordable, each location must be equipped with a minimum of three readers, which can be expensive due to the limited range of the tags.
Applications of UWB Technology:
- In some scenarios, exact location data, such as inventory management and manufacturing material flow, is crucial.
- UWB is frequently used in warehouses for precise tracking purposes.
Choosing the Right Technology:
- It’s important to assess specific needs and select a technology that best meets those objectives.
- UWB offers high precision and simpler proximity-level solutions, making it versatile for various applications.
Infrared Indoor Localization Technology
Infrared indoor localization technology uses a mechanism reminiscent of a TV remote, employing infrared light pulses for signal detection within enclosed spaces.
This technology is distinguished by its installation in each room: an IR receiver is placed to detect signals emanating from IR tags. Its functionality shines in enclosed environments, offering high accuracy at the room level.
The key reason behind its precision is the nature of infrared light, which cannot penetrate walls, thus ensuring that each signal is uniquely confined to its specific room.
Key Aspects of Infrared Technology:
- Signal Detection: Utilizes infrared light pulses for indoor signal detection.
- Room-Level Accuracy: IR receivers in each room ensure high accuracy due to the inability of infrared light to pass through walls.
The primary advantage of this technology lies in its unmatched accuracy. It excels in pinpointing an asset’s exact location within a room, significantly minimizing the likelihood of false positives that are often a challenge in systems based on radio waves. This feature makes it particularly effective when precise location data is paramount.
However, the implementation of infrared technology comes with its own set of challenges. One significant limitation is the need for a wired IR reader in every room’s ceiling. This requirement can pose considerable difficulties in retrofitting existing structures and is more seamlessly integrated into new constructions.
This technology is particularly beneficial in hospitals where clear room segmentation is essential.
Limitations and Suitability:
- Implementation Challenges: Requires extensive setup with a wired IR reader in each room’s ceiling.
- Ideal for New Constructions: Particularly suited for environments with distinct room divisions, such as hospitals.
2
Software Algorithms for Location Detection: Enhancing Precision and Versatility
Modern location detection software algorithms represent a pinnacle of technological advancement, offering unmatched precision in pinpointing locations. These algorithms combine the strengths of various technologies to achieve exceptional accuracy in diverse settings.
- GPS, Wi-Fi, Bluetooth, and Cellular Data: Harnesses a blend of these technologies for location tracking.
- Advanced Techniques: Utilizes machine learning, signal triangulation, and real-time data processing.
The algorithms overcome challenges, especially in indoor environments where issues like signal interference and physical barriers are prevalent. They are designed to easily navigate these complexities, thereby enhancing the accuracy and speed of location detection.
- Applications and Benefits:
- Indoor Navigation: Effectively handles signal complexities in challenging indoor spaces.
- Asset Management and Security: Integral in managing assets and securing areas.
- Real-Time Insights: Offers efficient and reliable location data for various applications.
These sophisticated software algorithms are essential in numerous applications, ranging from seamless navigation and wayfinding to robust asset management and security systems. They are crucial in providing efficient, reliable, real-time location insights, vital in our increasingly interconnected world.
Want to discover the diverse range of indoor tracking technologies available today?
Learn how each type can revolutionize your space management and navigation.
Contact Us
4
Future Trends and Innovations in Bluetooth AoA
As we look toward the future, Bluetooth Angle of Arrival (AoA) technology is set to revolutionize the landscape of indoor navigation, emerging as a cornerstone in developing precise indoor positioning systems. This technology is increasingly vital across diverse retail, healthcare, and smart building management sectors.
- Innovative Breakthroughs:
- AI-Driven Signal Interpretation: Integrating artificial intelligence and machine learning promises to significantly enhance the interpretation of AoA signals, thereby improving navigation accuracy in complex indoor landscapes.
- Hybrid Positioning Systems: Merging AoA with cutting-edge indoor positioning technologies like Ultra-Wideband (UWB) and Wi-Fi RTT will create multifaceted solutions, offering unparalleled versatility and robustness in indoor positioning.
- Sophisticated Signal Processing: Advanced algorithms are being developed to tackle indoor environmental challenges like signal reflection and multi-path interference, ensuring consistent accuracy across diverse settings.
- Technological Advancements:
- Component Miniaturization: Reducing the size of AoA components enables their integration into a vast array of devices, extending from smart wearables to mobile phones, thereby expanding the ecosystem of indoor positioning.
- Enhanced Energy Efficiency: Focus on developing low-energy AoA solutions is paramount to ensure sustainable, long-term operation, particularly critical for continuous indoor tracking systems.
- Upgraded Bluetooth Standards: Anticipated improvements in Bluetooth technology, including extended range, increased data transmission rates, and heightened reliability, are set to bolster the efficacy of AoA systems.
The trajectory of Bluetooth AoA technology is marked by a series of transformative innovations poised to redefine the accuracy and efficiency of indoor navigation systems.
By harnessing these advancements, we are on the cusp of a new era in indoor positioning, offering more intuitive, effective, and sophisticated navigation capabilities that will fundamentally change our interaction with indoor spaces.
Desire to stay ahead in the evolving world of indoor positioning technology?
Unlock the future of accurate and efficient navigation with our expertise.
Contact Us
5
IT Craft Expertise
IT Craft’s expertise can be pivotal in advancing the technology and methodologies used in indoor navigation systems in your next project.
Smart Navigation Systems: Innovating Indoor Navigation
From 2015 to 2018, Smart Navigation Systems, a UAE-based startup, collaborated with a team of seven to develop a groundbreaking indoor navigation platform. Specializing in location tracking and marketing within the indoor navigation industry, the project aimed to enhance visitor orientation in large facilities through a web and mobile-based solution.
Project Evolution:
- Developed an advanced location and positioning solution offering turn-by-turn guidance and BLE beacon-based notifications.
- Targeted facility visitors, owners, and shop owners, providing navigation aids, analytics, and promotional campaign management.
Achievements:
- We successfully launched native iOS and Android apps for users alongside a web-based administration panel for system management.
- Applicable across various facility types, including industrial settings.
Business Benefits:
- Introduced features like ‘find-my-car,’ outdoor-to-indoor navigation, white-label customization, and compatibility with diverse facilities.

"Our School Bus": Elevating School Transportation
In 2016, a forward-thinking startup, embarked on a mission to redefine school transportation. They assembled a skilled team of seven, specializing in location tracking and management, to bring “Our School Bus” to life. This innovative project wasn’t just about technology but peace of mind for parents and school efficiency.
Key Achievements:
- Over 1000 installations in 102 countries.
- Integrated technology: GPS for bus tracking, iBeacons for student detection.
Unique Selling Points:
- Real-time tracking for parents, enhancing child safety and peace of mind.
- Efficient fleet management for school administration, improving operational efficiency.
Market Impact:
- “Our School Bus” stands out for its comprehensive, user-friendly design, addressing the critical need for safe and efficient student transportation.

!
Conclusion
Our article highlights the significant strides in indoor navigation technology. Advanced systems like Bluetooth AoA, complemented by AI and expert insights from companies like IT Craft, are revolutionizing how we navigate indoor spaces.
These developments promise enhanced user experiences, improved safety, and greater operational efficiency, indicating a future where precise indoor navigation is integral to everyday life.










